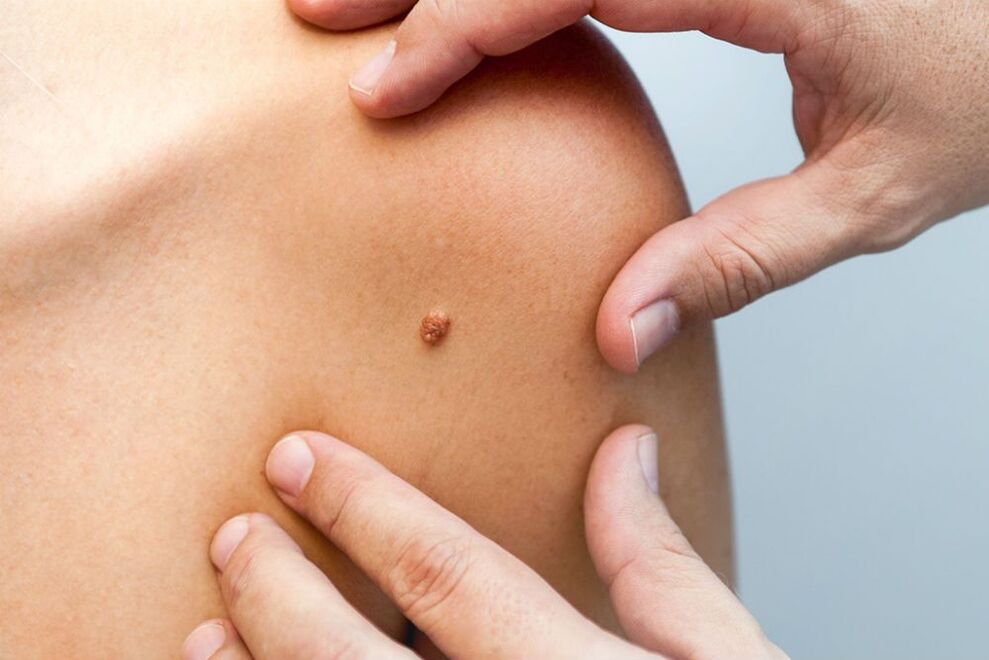
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a group of common pathogens that can infect the skin and mucous membranes. The pathology is mainly diagnosed in patients aged 20-30 years, as well as in children under 5 years old. According to statistics, around 22 percent of the world's population carries HPV. Many patients are affected by multiple strains simultaneously.
Currently, more than 190 genotypes of the pathogen are known. They differ in DNA structure, evolution and potential complications. 30 pathogens can infect the epithelium of the internal and external genitalia. It should be noted that many strains of HPV are characterized by pronounced carcinogenic activity. Thus, the virus often causes potentially fatal complications: malignant tumors of the vagina, vulva, anal tract, penis.
Causes of HPV
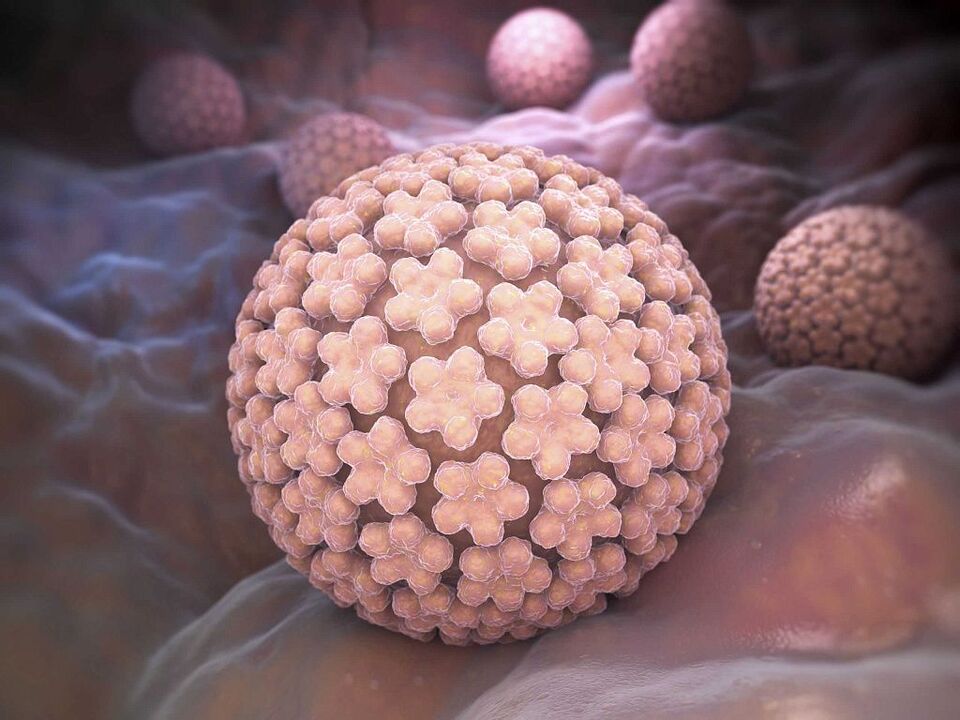
The only cause of the infectionhuman papillomavirusis contact with the causative agent of the disease. However, certain factors significantly increase your chances of becoming infected. Exactly:
- Refusal to use barrier contraception. Only a male or female condom, as well as special latex wipes, can protect against infection.
- Frequent change of sexual partners. If you do not pay enough attention to your own safety, the risk of infection increases significantly.
- Early initiation of sexual relations. Sexual intercourse during adolescence often leads to HPV infection due to an irresponsible attitude aimed at preventing the transmission of the pathogen.
- Non-compliance with hygiene rules. Insufficient personal care leads to the growth of pathogenic microflora on the skin and mucous membranes, which negatively affects susceptibility to the virus.
- Bad habits. The body's immune defenses are strongly affected by addictions: alcohol abuse, smoking and taking psychoactive substances.
- Weakened immunity. The causes of this disease can be vitamin and mineral deficiencies, previous illnesses and psycho-emotional overload.
- Long-term drug treatment. Hormonal drugs taken over a long period have a particularly pronounced effect.
- Traumatic injuries. Injuries to the mucous membranes and skin become the "gateway" of infection.
- Chronic stress. They also affect the immune system and hormonal background of the patient.
- Gynecological interventions. Risk factors for HPV include miscarriage or spontaneous abortion.
- Pregnancy. Often the disease first appears during pregnancy. Pregnancy is associated with increased stress on the body, which increases susceptibility to pathogenic flora.
Risks include certain diseases, such as uterine dysplasia. Regular preventive visits to a gynecologist and urologist help to significantly reduce the risks.
Symptoms
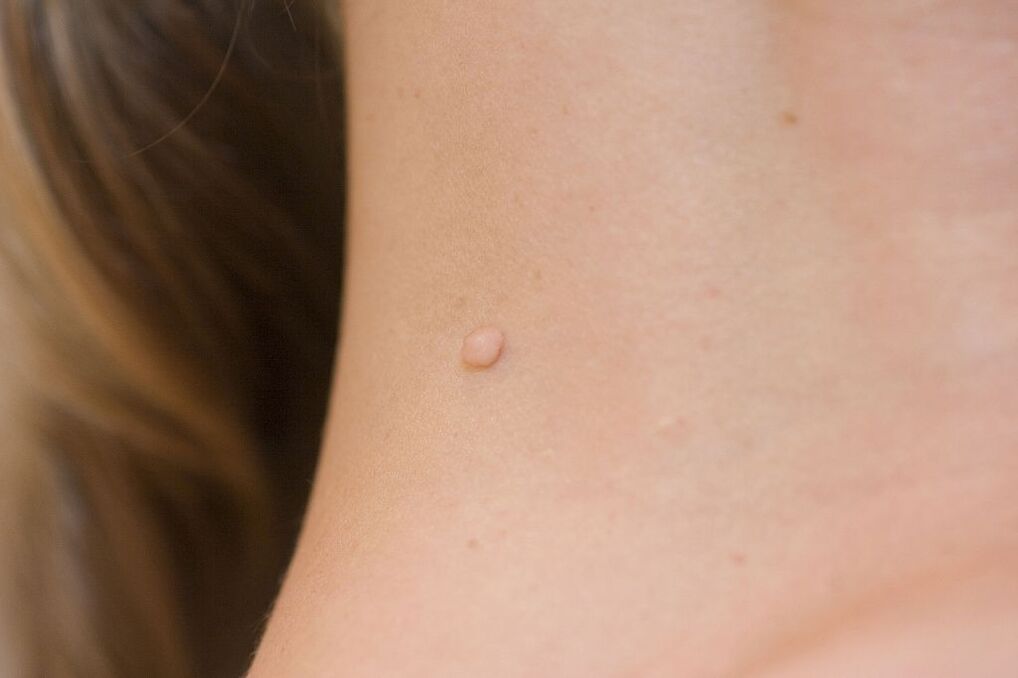
Of the total number of carriers of the pathogen, clinical manifestations of the papilloma virus are detected in only 5-10 percent of patients. The first symptoms may appear a few months after infection or after a few years. However, in this state, a person poses a threat to others. It can infect other people through contact. Symptoms can be divided into subjective manifestations, which indirectly indicate pathology, and objective characteristic manifestations of HPV. Subjective symptoms include:
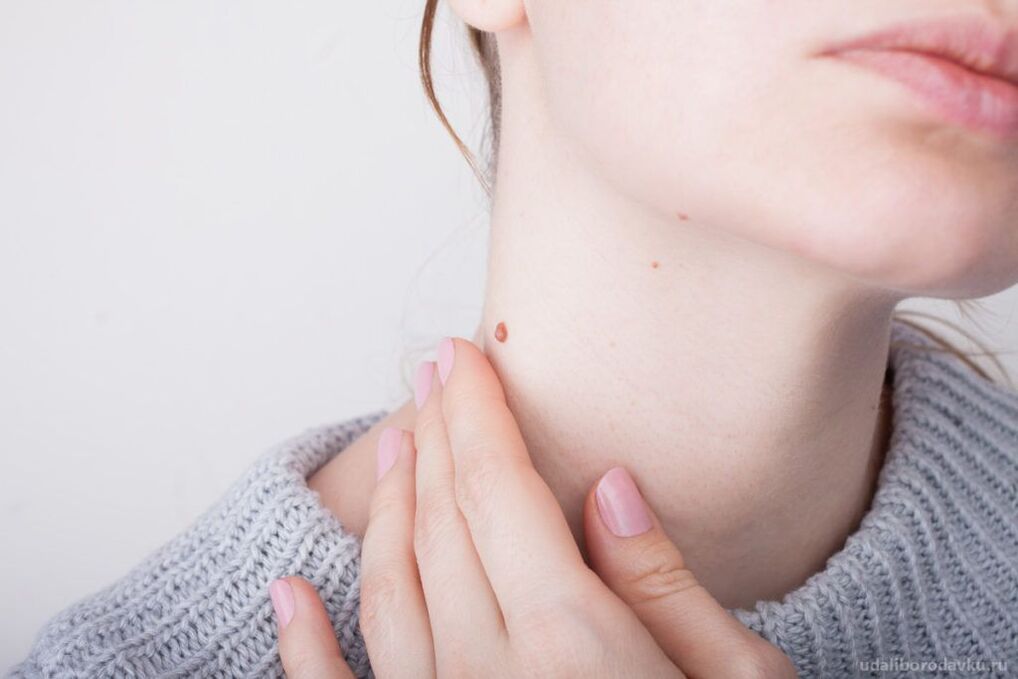
- Papules. These are single or multiple formations that protrude above the skin or resemble spots. They appear on the skin and mucous membranes of the urogenital area.
- Itchy skin. The patient often complains of itching in the genital area or other areas of the skin.
- Paresthesia. This is a sensitivity disorder in the affected area. Often the opposite manifestation occurs - dyspareunia. In this case, any contact brings pain.
- Urinary dysfunction. There is a burning sensation, itching and pain when emptying the bladder. If the urethra is affected, producing urine can be significantly difficult.
- Cracks. Hemorrhagic cracks appear on the skin and mucous membranes, causing severe pain.
Such clinical manifestations may indicate various diseases of the genitourinary system. Objective symptoms of HPV allow an accurate diagnosis. These signs include:
- Genital warts. It is an elevation above the surface of the skin, characterized by an elongated, finger-like shape. Located in the genital area. They differ in a specific pattern: variegated or loop-shaped.
- Papular warts. Appear on keratinized areas of the genitals. Can be flat or regular.
- Tasks. The nature of the spots varies. There are bright reds, browns with red undertones, pinkish reds, whites with gray.
- Bowen's disease. These are papules or spots characterized by a shiny or velvety surface. The color varies from red to almost black.
- Giant condyloma. It is a small formation that gradually increases in size and merges into one.
- Respiratory papillomatosis. In this case, the formations are localized in the oral cavity, respiratory tract and lungs.
In addition, HPV in women in advanced stages can manifest as uterine cancer. In 2008, it was discovered that this particular virus caused a malignant tumor. Cervical cancer does not present itself as an independent disease. The pathology is accompanied by heavy bleeding, pain in the abdomen and lower back, discomfort during intimacy, etc.
Transmission routes
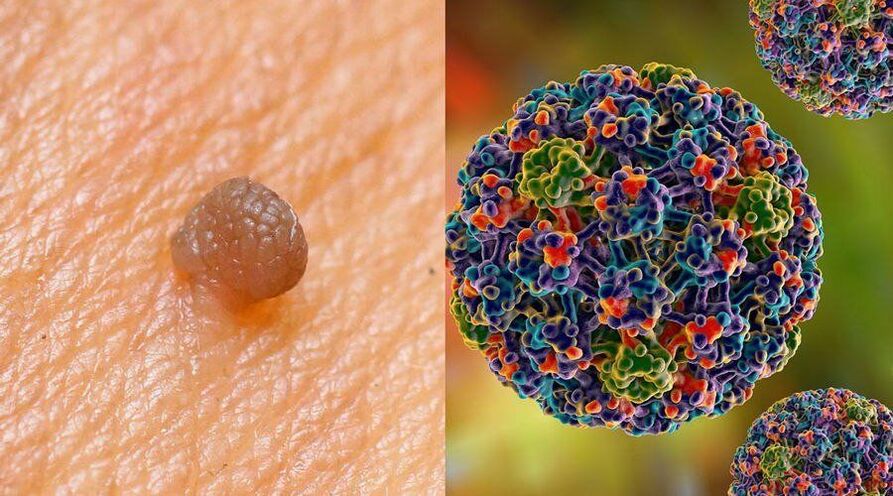
Doctors and scientists still argue about the contagiousness of the human papilloma virus. A number of experts believe that a single contact without barrier contraception with an asymptomatic carrier is enough for the probability of transmitting the pathogen to a healthy partner to reach 70 percent. Other doctors say that these risks are only relevant in case of contact with papilloma carriers. Statistics indicate that with regular proximity, transmission of the virus to a healthy person occurs within a period of up to 6 months.
Infection can occur in a variety of ways. How the papilloma virus is transmitted:
- Sexual transmission. The main method of infection is sexual contact. When you use a condom, the risk is reduced to 10 percent. However, the pathogen can also penetrate during other intimate manipulations, for example, when kissing.
- From mother to baby. A newborn can become infected with HPV from its mother as it passes through the reproductive tract. Typical consequences of this situation are cases of laryngeal papillomosis and anogenital warts.
- Contact and domestic progress. The virus is also transmitted through ordinary household contacts. Most often this happens in common areas. The risk of infection is particularly high in baths, saunas, gyms and swimming pools. Public toilets.
- Self-infection. This is the transfer of a virus from an affected area to a healthy area, which occurs during shaving and hair removal.
Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis is significantly influenced by the key capacity of HPV. It is the only virus that does not enter the blood and therefore does not cause an inflammatory process. In a simplified form, the pathogenesis of human papillomavirus is as follows:
- Infection. The source of viral agents can be another person or everyday objects. The risks of transmission are significantly increased by microtrauma to the skin and mucous membranes: wounds, cuts, cracks, acne.
- Incubation period. Pathologies that develop as a result of HPV entering the body usually have a latent onset. There is no exact length of the incubation period for this disease. The stage lasts 1 to 3 months or reaches 2 to 3 years.
- Chronic presence Despite the absence of clinical manifestations, the disease is constantly evolving. A person becomes a source of viral agents for others.
- Visual manifestations on the skin. The result of infection is the appearance of a benign or malignant formation at the site of entry of the virus.
At the initial stage, the pathogen affects the basal epithelial layer, localizing mainly on the mucous membranes of the genitals, oral cavity and conjunctiva. The viral agent is capable of replicating exclusively within the basal epidermis without entering the bloodstream. Due to this feature, the body's immune system cannot fully fight the pathology, but acts in an extremely limited way.
The main cause of oncological pathologies against the background of HPV is an increased release of specific proteins that affect the process of cell division. First, proteins responsible for blocking tumor changes, controlling the life cycle and protecting against replication in the presence of DNA damage are affected.
Classification
Due to the diversity of strains, HPV types also differ significantly from each other. Many experts use several classifications of the pathogen simultaneously. So, depending on the clinical picture, all cases of HPV can be divided into asymptomatic and with characteristic manifestations. There is a subclinical course in which periods of exacerbation are recorded. Depending on the location, we distinguish them:
- Skin. This type of human papilloma virus causes it to form on the skin of the infected person.
- Anogenital. In this case, papillomas are found mainly on the mucous membranes of the genitals and in the anal area.
External signs of HPV are often the main cause of discomfort for the patient. When evaluating a pathogen, doctors focus more on the carcinogenicity of the strain. Exactly:
- Types of HPV that are not capable of causing malignancies. These include strains 1 to 5, 10, 28 and 49.
- Types of pathogens with reduced oncogenic activity. They can cause cancer, but in extremely rare cases. Among these strains are 6, 7, 32, 40-44 and others.
- Characterized by moderate oncogenicity. The proportion of affected cells degenerating into cancer cells is quite high. The group includes strains 52-58, 30, 26 and others.
- Dangerous forms of human papilloma virus. It is these strains which mainly cause malignant tumor formations. This includes 16, 18, 64, 73 and others.
Diagnosis of human papilloma virus
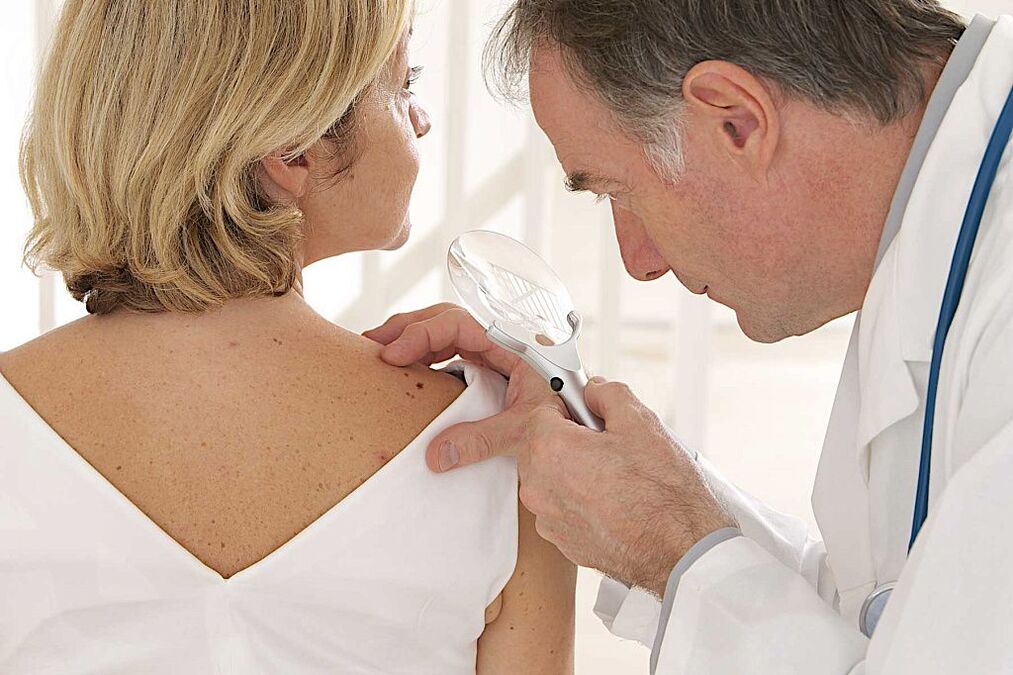
Various diagnostic techniques help identify papillomas in men and women. Thus, to establish a diagnosis in a patient presenting a latent form, only molecular biology studies are effective. The most common and well-known method is PCR. It aims to determine the genetic properties of material taken from the patient. PCR helps to identify not only the fact of infection, but also the specific strain of HPV. Subclinical and clinical forms can be diagnosed by methods such as:
- Simple colposcopy. Papillomas, warts and spots can also be detected during a routine visual examination. Colposcopy refers to the examination of the vaginal opening using a special binocular device. The examination may be accompanied by the collection of biological material intended for research.
- Extended colposcopy. During the examination, additional tests are used. A test using 3% acetic acid, which causes narrowing of unchanged blood vessels, is indicative. Additionally, an adrenaline test and a Chrobak test (if cancer is suspected) may be recommended.
- Cytological examination. To perform a diagnostic procedure, you will need material from the epithelium or skin cells. The sample is used to determine the DNA of the virus, as well as to exclude cancerous tumors. Typically, cytology detects only the most oncogenic types of viruses.
It is better to plan the collection of biomaterial for papilloma virus in women in the first half of the menstrual cycle, but not earlier than the fifth day. As a last resort, you can give biological material later, if there are more than 5 days before your period. Before the procedure, you should not douche your vagina. It is worth excluding sexual intercourse two days before collection. A similar rule applies to intravaginal ultrasound and colposcopy.
When diagnosing men with HPV, material is collected from the urethra. At least two hours should have passed since your last urination. It is important to avoid any privacy 48 hours before the test. Otherwise, the study could give false results.
Complications
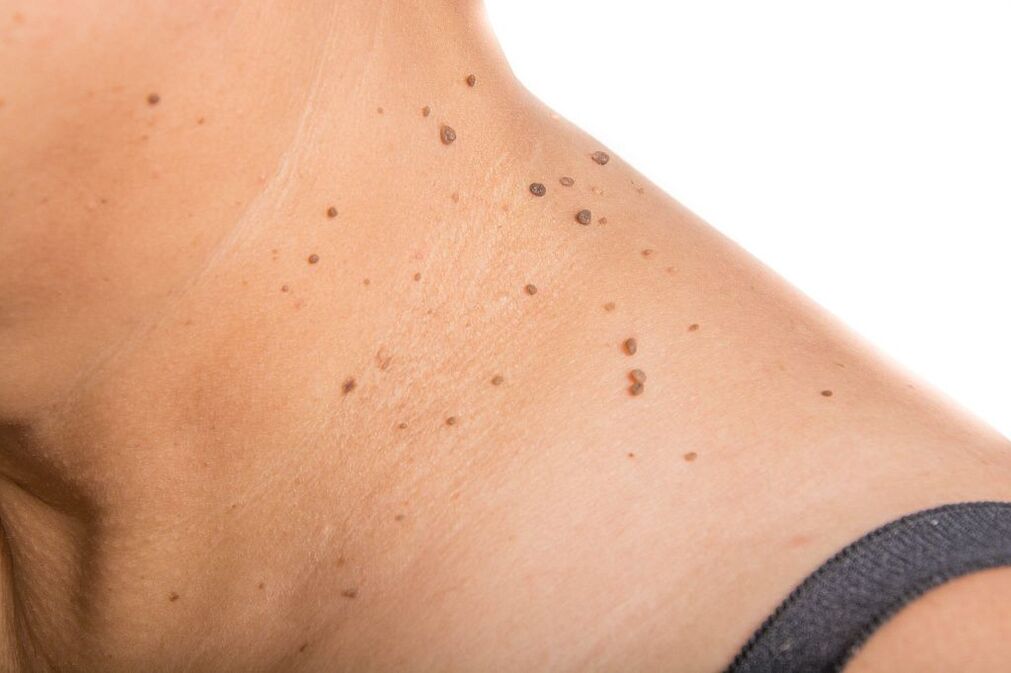
Complications of pathology include excessive growth of warts and papillomas. In rare cases, purulent-septic processes occur against the background of damage to the formation. Typical consequences of infection with oncogenic strains are the following conditions:
- Anal cancer. 80 percent of cases of detection of this malignancy are associated with HPV infection. In addition, negative factors influencing the occurrence of anal cancer include anal sex, smoking and hereditary predisposition. The disease may not manifest itself for a long time. Typical symptoms of the disease are bleeding from the rectum, itching and foreign body sensation.
- Vaginal cancer. 70 percent of patients with this diagnosis suffer from human papilloma virus. This disease generally affects women over 40 years old. Representatives of the fair sex over 70 years old are more susceptible to pathology. In the early stages, symptoms may be confused with menstruation. Additionally, pain in the pelvic region, constipation and vaginal tightness appear.
- Cancer of the oral cavity and pharynx. A third of diagnoses result from HPV infection. The patient complains of pain when swallowing and eating food. In a calm state, there is a sensation of a foreign body in the larynx. In later stages, general weakness, nausea and loss of performance appear.
- Penile cancer. 50 percent of cases are caused by viral agents. It is a rare malignant tumor, involving a tumor process located in the male genital organ. Pathology is typical for men over 60 years old.
HPV treatment
There is currently no effective treatment for HPV. Therapeutic tactics against the papilloma virus can be developed in two ways:
- Infection warnings. Unfortunately, even regular use of contraception and a careful approach to hygiene do not protect a person from infection. Of course, this greatly reduces the chances. However, most cases of transmission of the pathogen are recorded in people during adolescence, between 15 and 16 years old. Around the age of 25, the first symptoms already appear. For a pronounced effect, prevention should be carried out from an early age.
- Treatment of diseases caused by the human papillomavirus. If the strain causes malignant or benign formation, then treatment for the identified pathology is necessary. Papillomas are removed in cosmetic or medical offices. Cancerous tumors require complex, multi-stage treatment depending on the stage.
Of course, there is good news. So, people with normally functioning immune systems are able to cope with HPV on their own within two years. Patients infected as adolescents become free of the viral agent by age 30. Unfortunately, those who have recovered do not gain lifelong immunity.
Forecast
A significant proportion of strains are characterized by low or moderate oncogenicity. Only certain types of viruses are associated with an increased risk of developing cancer. These statistics allow us to give many patients a positive prognosis regarding HPV. Early detection of malignant tumors significantly increases the chances of cure.
The discovery of a virus capable of causing cell damage has three potential consequences:
- There is a virus, but it has not yet changed cell structure. In this situation, the patient will be classified as a risk group. If a carcinogenic type is identified, regular monitoring by a gynecologist or urologist is necessary. Additionally, you must undergo testing periodically.
- Changes in CIN-1 cells were detected at an early stage. Most of the time, this condition also does not require medical intervention. Typically, a follow-up exam is performed once a year to ensure that the condition does not progress.
- Pronounced changes in CIN-1 were recorded. To exclude dangerous conditions, a biopsy is required. The study will determine if the training is oncological in nature.
Prevention

You can prevent HPV infection by following key prevention rules. Important:
- Consult doctors timely. Women are recommended to schedule a visit to the gynecologist 1-2 times a year. Men should see a urologist on a similar schedule. If you have risk factors (frequent changes of sexual partners, refusal of contraception), you should consult the doctor more often.
- Minimize visits to public places - swimming pools, saunas, baths. If this is not possible, it is important to use your own towel, not to take other people's razors and not to sit on the surface with your naked body.
- Use contraception. Only barrier methods are effective. The use of oral contraceptives does not affect the strains.
- Refuse bad habits. Quitting smoking and moderate alcohol consumption will have a moderate impact on the body's condition.
- Increases the body's immune defense. Good nutrition, regular physical activity, adherence to a daily routine and exercise have a beneficial effect.
- Avoid stress. Psycho-emotional overload can negatively affect the immune system, so it is better to exclude them.
It is important to get tested periodically. If there have been situations where an infection could have occurred, then it is best to get tested for HPV. There are also people at risk. SO:
- patients aged 21 to 30 should have a PAP test at least once every five years (preferably by liquid cytology);
- people aged 30 to 65 must have a Pap test for HPV every three years with mandatory PCR for oncogenic forms (16 and 18).
HPV in pregnant women

As a rule, human papilloma in women does not pose any particular risk to procreation. Anogenital warts deserve special attention. They are located not only on the outer lips, but also in the vagina. In some cases, they are also accompanied by a bacterial component. Anogenital warts significantly increase the baby's risk of infection during delivery. This comes up against:
- Recurrent juvenile laryngeal papillomatosis. A similar situation is caused by four strains of HPV. Usually, the pathology is a consequence of anogenital warts or HPV of the genital type.
- Increased risk of developing cancer in adulthood. Infection with the virus at such an early age significantly affects susceptibility to cancer in the future.
Let's dwell in more detail on laryngeal papillomatosis. At the moment, it is not known exactly when transmission of the viral agent occurs. Infection can occur through the placental barrier or directly at the time of birth of the child. The first symptoms of the pathology are hoarseness. In difficult cases, the baby's voice disappears completely and breathing difficulties appear.
The disease is capable of progressing rapidly. A little later, the patient develops a constant cough and shortness of breath. Against the background of HPV, a child may suffer from asphyxia caused by blockage of the airways. Most often this happens when there are papillomas on thin legs.
To diagnose the disease, a special medical device called a laryngoscope is used. It can be replaced by a bronchoscope. The devices allow us to identify the main sign of pathology – the growth of the larynx (condyloma). Surgical treatment is usually recommended for the child. The warts are eliminated by destruction (freezing) or cut out. However, the aggressive nature of the disease often leads to relapses.
A pregnant woman infected with HPV with a high degree of oncogenicity should inform the obstetrician in the antenatal clinic. In this case, doctors will take all measures so that the virus does not affect the child's health.


















